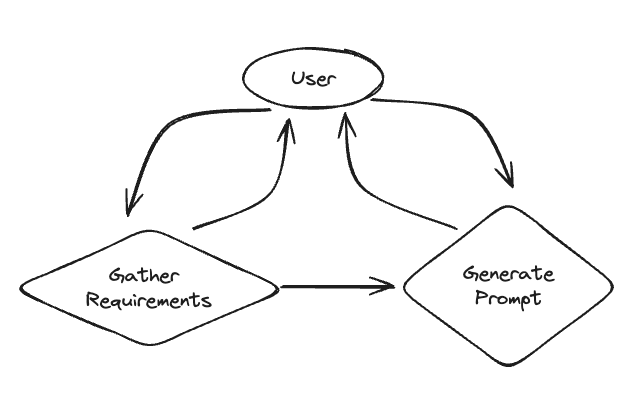
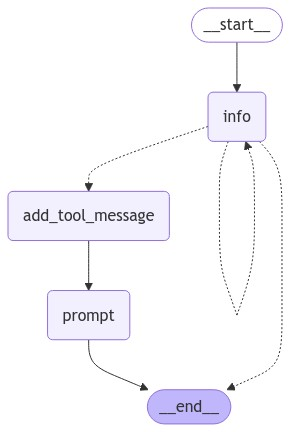
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
| from typing import List
import os
import uuid
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage, ToolMessage
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import END
load_dotenv()
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model=os.getenv("LLM_MODEL_NAME"),
api_key=os.getenv("LLM_API_KEY"),
base_url=os.getenv("LLM_BASE_URL"),
temperature=os.getenv("LLM_TEMPERATURE"),
max_tokens=os.getenv("LLM_MAX_TOKENS")
)
template = """
你的任务是从用户那里获取他们想要创建哪种类型的提示词模板信息。
你应该从他们那里获取以下信息:
- 提示词的目标是什么
- 哪些变量会传递到提示词模板中
- 输出不应该做的任何限制条件
- 输出必须遵守的任何要求
如果你无法识别这些信息,请要求他们澄清!不要试图胡乱猜测。
在你能够识别所有信息后,调用相关的工具。"""
def get_messages_info(messages):
return [SystemMessage(content=template)] + messages
class PromptInstructions(BaseModel):
"""Instructions on how to prompt the LLM."""
objective: str
variables: List[str]
constraints: List[str]
requirements: List[str]
llm_with_tool = llm.bind_tools([PromptInstructions])
def info_chain(state):
messages = get_messages_info(state["messages"])
response = llm_with_tool.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
# New system prompt
prompt_system = """Based on the following requirements, write a good prompt template:
{reqs}"""
# Function to get the messages for the prompt
# Will only get messages AFTER the tool call
def get_prompt_messages(messages: list):
tool_call = None
other_msgs = []
for m in messages:
if isinstance(m, AIMessage) and m.tool_calls:
tool_call = m.tool_calls[0]["args"]
elif isinstance(m, ToolMessage):
continue
elif tool_call is not None:
other_msgs.append(m)
return [SystemMessage(content=prompt_system.format(reqs=tool_call))] + other_msgs
def prompt_gen_chain(state):
messages = get_prompt_messages(state["messages"])
response = llm.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
def get_state(state):
messages = state["messages"]
if isinstance(messages[-1], AIMessage) and messages[-1].tool_calls:
return "add_tool_message"
elif not isinstance(messages[-1], HumanMessage):
return END
return "info"
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
memory = InMemorySaver()
workflow = StateGraph(State)
workflow.add_node("info", info_chain)
workflow.add_node("prompt", prompt_gen_chain)
@workflow.add_node
def add_tool_message(state: State):
return {
"messages": [
ToolMessage(
content="Prompt generated!",
tool_call_id=state["messages"][-1].tool_calls[0]["id"],
)
]
}
workflow.add_conditional_edges("info", get_state, ["add_tool_message", "info", END])
workflow.add_edge("add_tool_message", "prompt")
workflow.add_edge("prompt", END)
workflow.add_edge(START, "info")
graph = workflow.compile(checkpointer=memory)
# 画图
png_bytes = graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()
with open("graph.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(png_bytes)
import os
os.system("open graph.png")
cached_human_responses = ["哈喽!", "rag prompt", "1 rag, 2 none, 3 no, 4 no", "q"]
cached_response_index = 0
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": str(uuid.uuid4())}}
while True:
user = cached_human_responses[cached_response_index]
cached_response_index += 1
print(f"User (q/Q to quit): {user}")
if user in {"q", "Q"}:
print("AI: Byebye")
break
output = None
for output in graph.stream(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content=user)]}, config=config, stream_mode="updates"
):
last_message = next(iter(output.values()))["messages"][-1]
last_message.pretty_print()
if output and "prompt" in output:
print("Done!")
|