环境准备
UV安装
mac环境安装命令:
1 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh |
安装python 3.13
1 | 查看已安装的python版本 |
进入工作空间
1 | mkdir -p llm && cd llm |
创建工作目录:chatbot-tavily
1 | 使用指定python版本初始化工作目录 |
安装依赖
1 | 添加依赖 |
前置条件
在开始本文之前,请确保您已具备以下条件:
- Tavily 搜索引擎的 API 密钥。
配置环境
依然使用.env和dotenv实现llm配置即Tavily api key的传入。
.env
我是通过ollama本地部署qwen2.5:7b,这里可以根据实际情况自行变更。
1 | LLM_API_KEY=sk-ollama |
可以如此加载配置:
1 | from dotenv import load_dotenv |
对应的通过ChatOpenAI初始化llm实例:
1 | llm = ChatOpenAI( |
定义工具
定义网络搜索工具:
API 参考:TavilySearch
1 | from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch |
可以将结果打印出来:
1 | { |
定义图表
我们在上个文档里(LangGraph 案例:基本的聊天机器人)创建了StateGraph,现在需要在其基础上,添加搜索的工具。
API 参考:StateGraph |开始|结束| add_messages
1 | from typing import Annotated |
创建一个函数来运行工具
现在,创建一个函数,用于在调用工具时运行它们。具体方法是将工具添加到一个名为 的新节点,BasicToolNode该节点检查状态中的最新消息,并在消息包含 时调用工具tool_calls。它依赖于 LLM 的tool_calling支持,该支持在 Anthropic、OpenAI、Google Gemini 和其他一些 LLM 提供商中均可用。
API 参考:ToolMessage
1 | import json |
如果您将来不想自己构建它,您可以使用 LangGraph 预先构建的ToolNode。
定义conditional_edges
添加工具节点后,现在您可以定义conditional_edges。
边将控制流从一个节点路由到下一个节点。条件边从单个节点开始,通常包含“if”语句,根据当前图状态路由到不同的节点。这些函数接收当前图state并返回一个字符串或字符串列表,指示接下来要调用哪个节点。
接下来,定义一个名为 的路由器函数route_tools,用于检查tool_calls聊天机器人的输出。通过调用 将此函数提供给图add_conditional_edges,这将告知图,每当chatbot节点完成时,检查此函数以确定下一步要去哪里。
1 | tools`如果存在工具调用,则条件将路由到,`END`否则路由到 。由于条件可以返回,因此`END`您无需明确设置。`finish_point |
您可以用预先构建的tools_condition替换它,使其更加简洁。
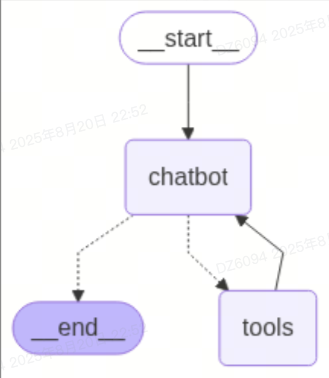
可视化图表(可选)
1 | # 画图 |
向机器人提问
现在您可以向聊天机器人询问其训练数据之外的问题:
1 | def stream_graph_updates(user_input: str): |
完整代码
完整代码(很丑):
1 | import os |
对话记录:
1 | User: What do you know about LangGraph? |
使用预建
为了方便使用,请调整您的代码,将以下内容替换为 LangGraph 预构建组件。这些组件内置了并行 API 执行等功能。
BasicToolNode被替换为预建的ToolNoderoute_tools被预建的tools_condition取代
最终的代码:
1 | import os |